Geography Class 04
Last class revision (5:13 PM)
International date line (5:36 PM)
- Diagramatic representation of international date line:
-

- It is an imaginary line of demarcation on the earth running from the North to South poles and demarcating the change of calendar day.
- It was agreed in 1884.
- IDL is not a straight line and follows a zig-zag path.
- If a person crosses IDL from West to East, she/he gains a day.
- If a person crosses IDL from East to West, she/he loses a day.
Daylight saving time (5:54 PM)
- It is the practice of shifting time by 1 hour ahead by forwarding the time in the clock just before the beginning of summer.
- It is practised in those regions where the length of the day varies between summers and winters.
Universe (6:05 PM)
- The limitless expanse of space surrounding us consists of the solar systems, stars, galaxies, etc.
- The Universe has around 100-400 billion galaxies with each galaxy having 100-400 billion stars.
- Origin of the Universe:
- Steady-state Theory:
- It was proposed by Fred Hoyle.
- The overall size and mass of the universe remain constant at any point in time.
- The universe has no beginning and no end and is always expanding, creating new stars and galaxies at the rate old ones become unobservable.
- Pulsating Theory:
- Proposed by Arthur Eddington.
- As per the theory Universe expands and contracts alternatively.
- Big Bang Theory:
- It was proposed by Gorgeous Lemaitry in 1927.
- According to the theory, 13.7 billion years ago, the Universe was an extremely compact, dense, and hot singularity.
- There was no matter, no space, and no time.
- 13.7 billion years ago, a cosmic explosion happened called as Bing bang.
- From that time the universe started to expand and is continuing today.
- The expansion subsequently created the forces of Physics including Gravity, the formation of elementary particles, atoms, molecules, gaseous compounds, stars, and galaxies.
- Hubble, in 1929, proposed that all observable stars and galaxies are moving away from earth.
- He discovered this through the phenomenon of the Red Shift.
- The rate of expansion of the universe is called Hubble's constant.
The life cycle of a star (7:16 PM)
- Diagrammatic representation of the life cycle of a star:
-
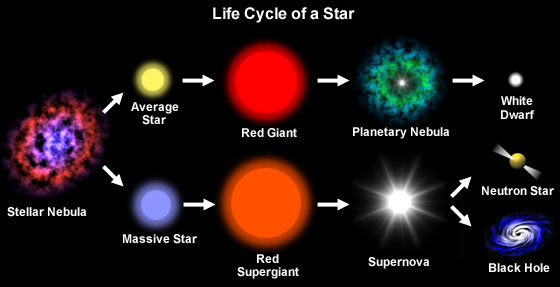
- A nebula is a huge cloud of gas and dust mainly consisting of hydrogen.
- The gas is pulled together by gravity and the entire nebula starts to spin.
- The spinning gaseous mass reaches a high temperature resulting in the formation of a hot core called ProtoStar.
- When the temperature of the core crosses 15 million degrees, a nuclear fusion reaction begins at the core resulting in the birth of a star.
- When the supply of hydrogen runs out the core contracts and simultaneously the outer shell expands due to the fusion reaction resulting in Red Giant.
- If it is a low-mass star with less than 10 times the mass of the sun the core collapses leading to the formation of a planetary nebula
- If it is an average star with less than 10 times the mass of the Sun, the core of the Red giant collapses and leads to the formation of a Planetary nebula which is a spherical shell of gas.
- After some time, only the core is left inside the shell, which is called a White dwarf.
- A white dwarf becomes a Black dwarf over some time.
- If the mass of a star is more than 10 times the Sun, the star results in Red Supergiant.
- A Red Supergiant results in a supernova explosion due to the explosion of the iron core
- If the remnant core after the Supernova explosion is between 1.4 to 3 times the mass of the sun, it leads to the formation of a neutron star, which is a very heavy dense body consisting of closely packed neutrons.
- If the remnant core after the supernova explosion is more than 3 times the mass of the sun, the core collapses under gravity leading to the formation of a black hole.
- A black hole is a body with infinite gravity and density that even light can not escape from it.
The topic of the next class: Universe to continue.